- Zeeve
- Posts
- Mapping Rollup Interoperability for Cross-chain Connectivity
Mapping Rollup Interoperability for Cross-chain Connectivity
Let’s dive into the most-talked topic in L2 space; rollup interoperability solutions. You may already know that the problem of ‘fragmented interoperability’ has always been a roadblock to seamless Web3 experience and the creation of innovative (or futuristic). Knowing this, Ethereum’s co-founder Vitalik Buterin, in his recent tweet rolled out his vision to enable cross-chain interoperability across Ethereum Layer2s. He basically talked about the following Ethereum Proposal Plans (EIPs) in the roadmap:
EIP-3370: Support for cross-chain transactions.
EIP-7683: Smooth transfer of assets across L2s.
EIP-3668: Efficient sharing of information and resources between L2s.
Here, the whole idea is to offer a standardized method to transact cross-chain. While this vision is promising, Vitalik Buterin has allocated it for the future. However, this article discusses the present rollup interoperability solutions that rollups can use for cross-chain interaction. We will cover both the native interoperability solutions and the pluggable interoperability layer.

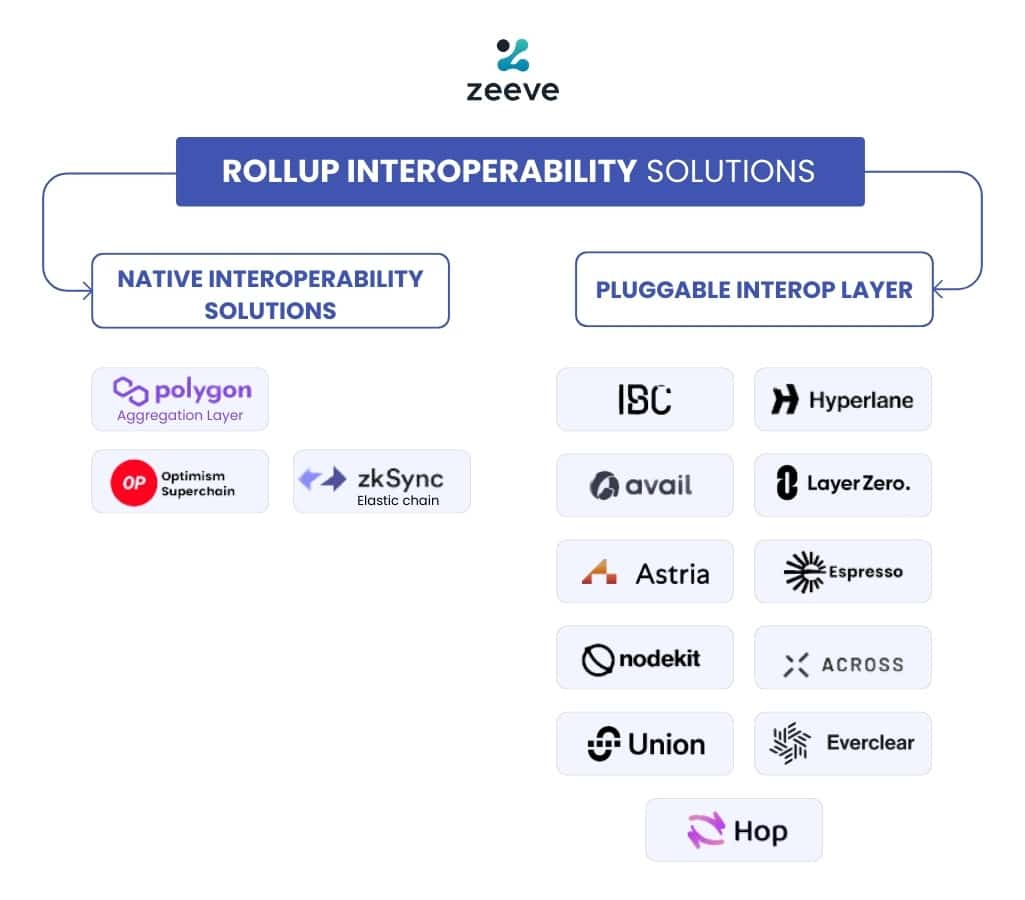
Native Interoperability solutions: For Ethereum Rollups
Polygon Aggregation Layer
Polygon is the pioneer in offering native interoperability for ZK-powered rollup chains building with Polygon CDK. The AggLayer is a novel interoperability solution that solves the fragmented interoperability issue by allowing sovereign chains to securely and seamlessly share liquidity, assets, users, and the state.
Chains connected with the Aggregation layer will benefit from atomic composability and fully uniformed cryptographic security while operating in an ecosystem of diverse L2/L3 chains that feels like using a single chain. Besides aggregating ZK proofs from all the interconnected chains, the AggLayer also ensures near-instant cross-chain transactions. Instead of involving any 3rd party bridging solution, AggLayer implements a single bridge contract that works for all the chains without posing any security risks.
Initially, Polygon zkEVM was the only chain connected to AggLayer, but gradually, other chains started plugging into the layer. For example, Astar is launching its Astar zkEVM chain using Polygon CDK, which will integrate the Aggregation Layer. Also, TON Applications Chain (TAC) has announced that their zk-powered L2 will connect to AggLayer. Let’s see the main benefits of AggLayer:
Full sovereignty: Interconnected L1 and L2s using AggLayer can tap into unified liquidity. As needed, these chains can bootstrap liquidity for their applications and specific use cases.
Rich UX: AggLayer allows users on any chain to interact with Polygon CDK chains directly without involving the cumbersome bridging process. Hence, UX remains simple and intuitive.
High-speed atomic transactions: AggLayer offers unmatched speed with atomic transactions, allowing users to execute cross-chain transactions in less than 1 second.
ZKsync Elastic chain
ZKsync’s Elastic chain offers an infinitely scalable network of diverse ZK chains; be it rollups, validiums, and volitions. Although new, over 20+ chains are soon to be built on the ZK sync Elastic chain. All L2/L3s building with ZKsync Elastic chain are secured by math and are natively interoperable to offer a uniformed and intuitive UX that enables low-cost, trustless interoperability across independent chains building with ZK Stack framework. Each Elastic chain is based on a perfectly designed architecture that allows ZK Stack chains to expand their scaling capabilities limitlessly by adding new instances as required. Let’s highlight the main features of ZK sync Elastic chain:
Intuitive UX: Users on an Elastic chain network can use a single address across multiple interconnected chains. Plus, a single signature can be used to transact or interact with any smart contracts in the ZK Sync ecosystem. Also, fees can be paid in any liquid token or they can benefit from gasless transactions if offered by the application.
Low-cost transactions: The cross-chain approach in Elastic Chains does not make much difference in the transaction cost of a single ZK chain. Further, the growing number of chains and their scalability will not raise the cost.
Secured by math: Transactions on Elastic Chains are verified and enforced by mathematical cryptography techniques with zero human assumptions. In the long run, ZK Sync plans to facilitate verification through users’ smartphones.
Optimism Superchain
Optimism Superchain is the next big innovation to enable natively interoperability across all types of chains; whether OP chains, Bedrock or Optimistic Virtual Machine (OVM). Superchain has introduced a concept that allows for the creation of a single, unified network of standalone OP Chains that share a common ecosystem and its resources like bridges, decentralized governance, upgrades, a messaging layer, and more. This structure is designed to provide untapped interoperability across different L2/L3 OP chains, allowing them all to communicate and transact similarly to the internet, which allows web2-based to communicate with each other without issues. There are around 54 chains in the Superchain ecosystem, both in the testnet and mainnet phases. Let’s see what benefits Superchain offers to OP Stack rollups:
Interconnected system/efficiency: OP Superchain allows ‘sub-chains’ or L2/L3s to seamlessly transact with each other and thereby contribute to enhanced processing capacity in the ecosystem.
Consistent security: As discussed, the interconnected OP Stack Layer2s adheres to shared security based on Ethereum. This maintains trust and unformed security across the entire Superchain ecosystem.
Dynamic scalability: Similar to the ZKsync Elastic chain, Superchain can expand easily with the addition of more chains. The scalability, security, and interoperability of existing networks will not be impacted because of this.
Possible Challenges:
Composability fragmentation: While all the native interoperability solutions talk about enabling interoperability, composability still feels like a missing piece. By composability, we mean a rollup’s ability to initiate transactions on different rollups, which is a solid form of interoperability. Hence, Protocols definitely need to focus more on standardization to support enhanced composability.
Integration issues with other rollups: Right now, native interoperability is based on framework.
Polygon AggLayer connects Polygon CDK chains, Superchain connects OP Stack chains, and Elastic chain connects ZK Stack chains. However, there must be a new standard that allows the coordination of ZK Chains with Optimistic rollup chains so that actual unification can be achieved.
Scalability & latency concerns: Massive growth of chains in an interconnected ecosystem can lead to a lack of scalability and high latency. As of now, all the protocols are handling the tractions and users well, but it’s a concern for the future.
Pluggable Interoperability solutions: For all kinds of rollups
IBC Protocol
Inter-blockchain communication (IBC)is an interoperability protocol that supports authentication and data transportation between two different blockchains. Layer1 or Layer2 chains building with IBC can facilitate permissionless, highly secure, and feature-rich interaction for users. 110+ chains, including both EVM and non-EVM chains have already been using IBC, contributing to the 30M+ daily token transfers. Some of the leading names include Cosmos, BNB Smart chain, Polkadot, and Avalanche. Regarding features, IBC offers universal interoperability, permissions access, and reliable security.
Hyperlane
Hyperlane is a permissionless cross-chain interoperability layer designed to serve modular blockchains. With 50+ chain connected, $2b+ value bridged, and support for more than 5+ virtual machines, Hyperlane is positioning itself as a leading interoperability layer. Any L2/L3 rollups, appchains, or even Layer1 blockchain can plug-in Hyperlane’s interop layer to connect to different chains to share assets, resources, or essential information. Hyperlane supports both EVM and non-EVM chains, including Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, Avalanche, Base, and more.
Avail Nexus
Avail Nexus is a permissionless verification layer that unify different rollups leveraging Avail DA as the base. Nexus essentially offers a custom ZK coordination system for rollups created on top of Avail. This enables for a seamless state verification and systematic sequencer confirmation regardless of all the rollups, whether it’s about engaging with a single rollup, exploring multiple rollups, or processing transactions across various Layer1 blockchains. Avail supports all the rollup protocols, including Arbtirum, Optimism, ZK Sync, and Polygon CDK.
LayerZero
LayerZero is an open-source, omnichain interoperability protocol designed to support development of interoperable applications with low-level communication primitives. LayerZero is one of the preferred solutions for cross-chain connectivity with $50B+ value transferred, 70+ supported blockchains, and over 200 applications built on it.
Layer2/Layer3 rollups using LayerZero can send arbitrary data, tokens, and external function calls quickly through its advanced omni-chain messaging. Meanwhile, they retain full control and autonomy over their applications through immutable smart contracts that eliminate all kinds of censorship issues. Further, LayerZero stands out with the below main features:
Omni Network
Omni Network is an interoperability infrastructure for building chain abstracted web3 applications. The platform stands out with its single unified network that has gathered around 7.5M transactions, 400K users, and over 30 ecosystem projects. Omni Network coordinates different rollups across a single, cohesive layer, thereby allowing developers to easily source liquidity, assets, and users from the Ethereum ecosystem. Omni also equally focuses on performance & security. Hence it uses the re-staking approach to power next-gen blockchains. Inheriting battle-tested security from Ethereum and combining it with a high-performance rollup architecture allows for unparalleled speed and performance necessary for today’s rollups. It offers rollups with the options to expand, upgrade, and innovate without making any changes in their smart contract.
Espresso
Espresso serves as a coordination layer for various blockchains that enhance interoperability across them while retaining fast-finality, sovereignty, scalability, and credible neutrality. Espresso comes with a free and open market for decentralized sequencing. This sequencer mechanism allows chains to communicate and coordinate for transaction ordering. With Espresso, rollups see the same level of efficiency for both the bridging and atomic transactions. Whether you build a rollup, appchain, or a L1 blockchain, Espresso will allow users on your network to exchange values without seeing any difference in performance, speed, or latency.
Nodekit
Nodekit offers infrastructure build composable Layer2s that uses the power of Javelin; the superbuilder. Javelin can plug into various products, be it L2s, centralized/decentralized sequencer, shared sequencers, and based preconfs. Hence, rollups and appchains using Nodekit can leverage a sequencer-based interoperability layer to share liquidity, value, and assets while also having the flexibility to build a variety of use cases that were not possible due to fragmented interoperability. By utilizing Nodekit, rollups can execute cross-rollup and atomic transactions while retaining the security & scalability. There are around l2 rollups that have implemented Nodekit, such as Morph, Naka Chain, Alpha, PlayAI, and more.
Across settlement
Across settlement is an interoperability layer offered by Across that enables cross-chain connectivity powered by intents. Across claims to be the most production-ready and modular settlement layer for enabling cross-chain intents for both OP and ZK rollups. With 6M+ transactions, an average fill time of less than 1 minute, and <$1 cost is what makes Across a feasible option. Cross-chain intents settlement, modular design, aggregated & optimistic verification, and cross-chain management are the top features of Across settlement. Across supports all the leading rollups and blockchain networks like Ethereum Mainnet, Optimism, ZK sync Era, Polygon, Base, Zora, etc.
Union
Union is an open-source, modular interoperability layer designed for ZK rollups. However, Union goes beyond to enable interconnectivity across next-gen blockchains, appchains, and rollups. Union leverages zero-knowledge cryptography and advanced consensus verification to offer a fast, trustless, and permissionless approach to interoperability. Union’s infrastructure layer unifies diverse modular networks to unlock horizontal scalability for them. Popular supported-chains are Ethereum, Polygon, Scroll, Celestia, Canto, Movement, and more.
Everclear
Everclear (formerly known as Connext) serves as a clearing layer that unifies global netting, liquidity, and capital flow settlement across different rollup chains. Through the netting approach, Everclear claims to cut down the transaction cost and complexity associated with CEXs, market makers, and solvers by 10x. Additionally, Everclear supports the development of programmable settlement, and it powers permissionless liquidity as well as expansion to support new use cases. Everclear has extended its support for all the leading ZK and OP rollup protocols chains like Optimism, Polygon, ZK Sync, Arbitrum, Mantle, and more,
Hop protocol
Hop is an interoperability solution that supports token transfer across various rollup chains. The protocol includes a combination of tools and novel algorithms that complements the bridging approach while allowing users to freely move their assets across blockchains, rollups, and appchains. Further, Hop includes modified liquidity tech, decentralized pools, and an advanced token minting strategy to make inter-chain communication even more efficient. Hop supports all the prominent rollup networks like Ethereum, Arbitrum, Polygon, and Gnosis.
Benefits and Possible Challenges:
● Limited adoption: The major challenges that pluggable rollup interoperability solutions face is the lack of their widespread adoption and support from the community. As new and independent solutions, they often face issues in building trust and maximizing the adoption. To overcome this, pluggable interoperability solutions focus more on improving the TPS, performance, low-cost processing, and various advancements on their protocol from time to time.
● Competition: Alternative interoperability solutions have to be in competition with established players like Polkadot, Optimism, ZK sync as they offer native interoperability solutions. However, these pluggable solutions have been able to differentiate their service with innovative features like universal interoperability, enhanced liquidity, easy customization, better standardization, and lower cost.
● Security concerns: Unlike native interoperability solutions, pluggable interop layers cannot inherit Ethereum-based security. But, these solutions often provide configurable trustlessness, allowing you to adjust the security parameters according to risk possibilities.
Power interoperability in your L2/L3s rollups with Zeeve RaaS
If you are planning to launch interoperable rollups or you want to add interoperability to your existing chain, Zeeve RaaS can assist. You can either build a rollup with native interoperability or you can choose from a range of pluggable interop layers from our RaaS stack. Zeeve RaaS supports all the solutions mentioned in this article, be it LayerZero, Espresso, Avail Nexus, Espresso, and Nodekit. For native interoperability, you can launch an OP Stack chain, ZK Stack L2, Arbitrum Orbit chain, or CDK chain while enabling the connection to the Aggregation layer, Superchain, or Elastic chain. For more information about our rollup offerings, connect with us. Or send your queries via mail.